La ecuación matemática que describe esta relación es:
Esta ley tiene el nombre del físico alemán Georg Ohm, que en un tratado publicado en 1827, halló valores de tensión y corriente que pasaba a través de unos circuitos eléctricos simples que contenían una gran cantidad de cables. Él presentó una ecuación un poco más compleja que la mencionada anteriormente para explicar sus resultados experimentales. La ecuación de arriba es la forma moderna de la ley de Ohm.
Esta ley se cumple para circuitos y tramos de circuitos pasivos que, o bien no tienen cargas inductivas ni capacitivas (únicamente tiene cargas resistivas), o bien han alcanzado un régimen permanente (véase también «Circuito RLC» y «Régimen transitorio (electrónica)»). También debe tenerse en cuenta que el valor de la resistencia de un conductor puede ser influido por la temperatura.
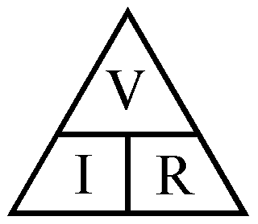
Ohm's law states that the electrical current flowing between two points in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the voltage between these points, there being a constant of proportionality between these two magnitudes. This proportionality constant is the electrical conductance, which is opposite to the electrical resistance.
The mathematical equation describing this relationship is:
where I is the current passing through the object in amperes, V is the potential difference of the terminals of the object in volts, G is the conductance in siemens and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω). Specifically, Ohm's law states that the R in this ratio is constant regardless of the corriente.1
This law is named after the German physicist Georg Ohm, who in a treatise published in 1827, found values of voltage and current passing through a simple electrical circuits containing a large number of cables. He presented a slightly more complex equation as mentioned above to explain the experimental results. The above equation is the modern form of Ohm's law.
This law holds for circuits and passive circuit sections that either have no inductive or capacitive (resistive loads only is) or have reached a steady state (see also "RLC circuit" and "Transitional arrangements (electronic)" .) Should also be noted that the value of the resistance of a conductor can be influenced by temperature.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario